We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
Technical FAQs
FAQs
Please find below some of our frequently asked technical questions.
If you can't find the answer you need or wish to discuss our customisation capabilities please contact our technical team: tech@pulsardevelopments.com
01189 795319
Example: A 20Ah battery can supply 1A for 20h.
Volumetric energy density is how much energy can be stored in a volume. The units are Watt-hours per litre (Wh/l).
Gravimetric energy density is the amount of energy that can be stored per unit mass. The units are Watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg).
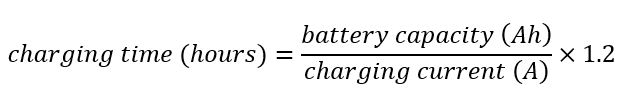
1.2 is a factor that adds 20% extra time to ensure the charge cycle is fully complete.
Carefully check the chemistry and capacity of your battery when selecting a charger.
On each product there is a label that indicates the year and week of manufacture.
A power supply will deliver a fixed voltage up to a maximum current and delivers only the current required by the device. A device requiring 0.8A will function perfectly using a 1A power supply providing the output voltage is correct.
If you're unsure please contact our technical support team: tech@pulsardevelopments.com
01189 795319
08:00-17:30, Monday – Friday
This depends on the chemistry of the battery. A lead acid battery in ideal conditions should not be drained further than 50% in order to prevent sulphating. Other chemistries including Lithium-ion, Nickel metal hydride and LiFePO4 can be used until very low percentages and recharged with no issue. Nickel-cadmium batteries are prone to memory effects meaning they should be drained fully occasionally to ‘reset’ their capacity memory.
If you are storing a lead-acid battery it should be stored with as much charge as possible at ~20˚C and will last between 6 months and 2 years depending on the quality of the battery. Other chemistries including NiCd, NiMH, Li-ion, LiFePO4 should be stored in cool dry places with approx. 40% charge. In this state NiCd can last between 1.5 to 3 years, NiMH last approx. 3 - 5 years while Li-ion, LiFePO4 can last up to 2 - 5 years. Storage under ideal conditions can double these estimates. The timeframes above are drawn from experience in household conditions. Shelf life will depend on the quality of individual products – consult the manufacturer guidelines for more specific information about your product.
Yes, Pulsar Developments has an experienced team of engineers that can fit a wide range of output connectors. All you need to do is provide a connector type/spec (preferably with a product code) and a polarity requirement and we can fit it for you.
Please contact our technical support team: tech@pulsardevelopments.com
01189 795319
08:00-17:30 Monday – Friday
Pulsar Developments can source and supply a wide range of lead acid, NiMH, and Li-ion batteries or cell packs. Please contact Pulsar Developments directly for more information on custom made battery packs.
Yes, we have support from Mascot’s experienced design team and can either configure standard products or find a non-standard solution by generating a custom design.
Please contact our technical support team: tech@pulsardevelopments.com
01189 795319
08:00-17:30 Monday – Friday
Yes, there are multiple parameters that can be adjusted to meet your needs. The settings that can be programmed by Pulsar Developments include negative voltage drop (-dV), temperature gradient (dT/dt), safety timer, start timer and top off charge timer.
Yes, as batteries rely on chemical reactions.
Cold - the colder they are the slower these reactions are reducing electrical performance.
Hot - The hotter a battery is, the more energy is lost to the surroundings. This is due to faster reactions occurring increasing the self-discharge rate of the battery – lowering the effective capacity of the battery.Each battery manufacturer will provide an operating temperature range for the best performance.
Yes, care must be taken to safely handle batteries to prevent the terminals short-circuiting. Any metal or conductive material such as coins in pockets can link the anode and the cathode together and damage the battery and those nearby. It is important that battery terminal covers are fitted for transporting batteries.
Where possible , terminal covers should be fitted to batteries when being transported.While they are similar it is not recommended to do this exchange without also changing the charger being used. Chargers for NiMH need to be much more sensitive to correctly detect the end of charge and so a NiCd charger cannot be used on NiMH. However, a NiMH charger could be used to charge NiCd batteries.
No, Li-ion batteries are much more energy dense than other chemistries and work at different voltages. Usually entire systems and chargers are designed specifically for lithium-ion batteries and using them in a setting without these design considerations can lead to damaged devices and could pose health concerns to those nearby.
No, as each battery chemistry and capacity require a unique charging solution. Charging with the wrong charger will cause damage to the batteries. Batteries of the same chemistry at different ages will have varying capacities and so can give false charging signals – potentially damaging the batteries and device via overcharging.
Batteries in a device should always be of the same chemistry at the same voltage, capacity and of the same age.
IP (ingress protection) classifies and rates the level of protection of mechanical casings and electrical enclosures against intrusion, dust, accidental contact, and water. The first digit gives the level of intrusion protection and the second digit gives the amount of moisture protection. Higher numbers/digits indicate greater protection.
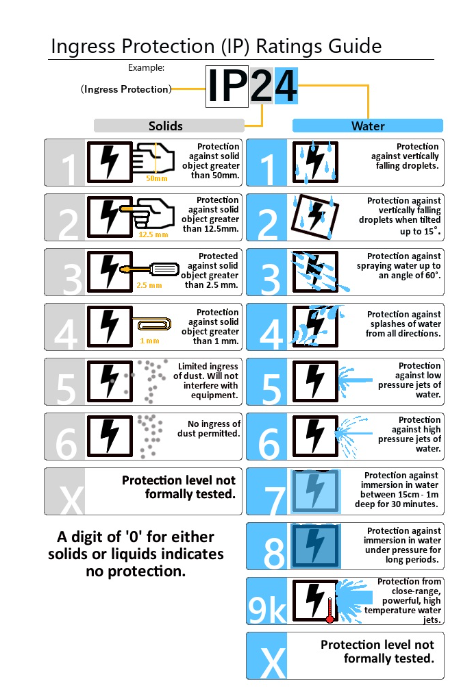
Pulsar developments have prepared a technical document that you can review to learn more information about this here.
An exact alternative is functionally identical and any minor differences, such as size, will be highlighted. An upgrade alternative is a newer design product or a product that has extra approvals such as medically approved and manufactured by the same manufacturer. A suggested alternative is a product that is functionally similar with similar form and fit and all differences will be highlighted for the customer to make the decision if it will work in their application.
Battery Charging rates
1.1 LEAD ACID (SLA)
First identify the voltage of the battery to be charged. The voltage which should be clearly marked on the battery. The charger will need to be rated according to the voltage of the battery in order to charge it successfully e.g. a 12V battery will need a 12V charger. Next identify the capacity of the battery in Ah and then divide this number by 4. This will give the maximum charging current accepted by the battery without damaging it unless otherwise stated by the battery manufacturer. Generally, exceeding this limit will reduce the lifespan of the battery and can potentially make the battery unsafe. A 24V, 20Ah lead acid battery will need a 24V 5A charger. If an exact match of charging current to the battery capacity cannot be found, a charging current that is a bit below can also be used. This will increase the charging time of the battery but is perfectly safe to use.
Three-step charging is recommended for lead acid batteries to give the shortest possible charging time while keeping the battery healthy. 1. The battery is charged at a constant current which is the maximum charging current allowed. This is commonly referred to as boost charging. This charges the battery at a high rate until it approaches charge voltage at ~ 80% charged. 2. When the battery approaches charge voltage the constant current changes into a constant voltage, a little above nominal battery voltage. This allows the charging current to decrease as the remaining charge is given to the battery which helps to prevent overcharging. 3. The charger detects that the charging current is much lower than expected which indicates the charge cycle is complete. When this occurs, the charger cuts off the current to prevent overcharging the battery.
1.2 LITHIUM-ION (Li-Ion)
Lithium-ion batteries are made up of many cells combined. When selecting a charger, the first step is to identify how many cells are present in the battery. Each cell has a charge voltage of 4.2V and as batteries are in a series circuit the number of cells determines the overall charge voltage. A 10 cell Li-Ion battery would have a charge voltage of 42V whereas, a 2 cell would be 8.4V. The charger chosen must be at the correct voltage to charge the battery fully. The charging current can be determined by identifying the battery capacity ( ) and dividing it by 2 to give . This is a good estimate to prolong the life of your battery even though it is a bit slower. Some manufacturers recommend a charging current of for some models and if that is the case ensure that the charger has detection methods to prevent over charging.
Example: To charge a 4 cell 7Ah Li-Ion battery, a charger should be chosen that has a voltage of 16.8V and a charge current of 3.5A.
1.3 LITHIUM IRON PHOSPHATE (LiFePO4)
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are quite like lithium-ion batteries as they are both based on lithium chemistry however, there are differences that need to be accounted for when charging. Each cell in a LiFePO4 battery requires a charge voltage of 3.65V and as the batteries are in a series circuit the number of cells determines the overall voltage. A 4 cell LiFePO4 battery would be rated at 14.6V charge voltage whereas, a 7 cell would be 25.55V. The charger chosen must be at the correct charge voltage to charge the battery fully. The charging current in Amperes is determined by the battery capacity (C) in Ampere-hours. A good estimate to prolong the life of a LiFePO4 battery is to use a current of 0.5C up to 0.8C Amperes. Some manufacturers recommend a charging current of C or greater for some models and if that is the case ensure that the charger has appropriate detection methods to prevent over charging.
Example: To charge a 4 cell 7Ah LiFePO4 battery, a charger should be chosen that has a charge voltage of 14.6V and a charge current of 3.5A using (0.5C charging current).
1.4 NICKEL METAL-HYDRIDE (NiMH) & NICKEL-CADMIUM (NiCd)
NiMH batteries are the most complicated to charge as detecting when they are fully charged is difficult and requires a smart charger to prevent overcharging. The methods most commonly used to detect the end of charge in an NiMH/NiCd battery is a voltage-drop (-dV) or a rate of temperature increase (dT/dt). Modern NiMH chargers are more sensitive than older NiCd variants in order to give the finer resolutions needed to detect the end of charging. This means that a NiMH charger can be used to charge NiMH and NiCd batteries, but a NiCd charger can only be used to charge NiCd batteries.
For more information about NiMH charge termination please look at the extra resource available on the Pulsar Development website.
Batteries including nickel have large quantities of tiny crystals to increase surface area. This allows more of the anode to be in contact with the electrolyte however, over time larger crystals form reducing the surface area and thus reduces the performance of the battery. To minimise this effect a very rapid charge is recommended via constant current.
To select an appropriate charger, begin by identifying how many cells are in the battery. This should be written on the battery pack or appliance used. Each NiMH cell requires a charging voltage of approximately 1.4 - 1.6V. As these batteries are usually wired in series the total number of cells will determine the overall charging voltage. The capacity ( ) of the battery in Ampere-hours is used to give the charging current to be used. A good estimate is to use between 0.5 and 1 Amperes, though a more specific current may be given by individual manufacturers and should be checked. Charging at this rate is important as it ensures that there is a detectable temperature increase or voltage drop to determine end of charge - preventing overcharging. When a voltage-drop or temperature increase is detected the high current charging is stopped and a topping off current of approximately C/10 Amperes takes over. This runs for approximately 1 hour (or programmed custom time), to provide the remaining charging to take the battery to full capacity. It is recommended that an override safety timer (OST) is set to ensure the cell pack is not damaged by overcharging. Pulsar Developments can set custom OSTs to meet specific requirements.
